How High Intensity Interval Training Helps to Boost Metabolism
[ad_1]
The results of a research in gentlemen demonstrate how skeletal muscle adapts to significant-depth interval teaching, these as improvements to procedures that are vital for the regulation of muscle contraction and fat burning capacity.
The results indicate that high-depth interval instruction raises the selection of skeletal muscle proteins that are necessary for energy muscle contraction and rate of metabolism, and chemically adjustments critical metabolic proteins. This could demonstrate higher-intensity interval training’s advantageous consequences on fat burning capacity and set the groundwork for much more study looking at how exercise has an effect on these processes.
Workout has various valuable effects that enable in protecting against and dealing with metabolic health conditions which are most likely brought about by changes in skeletal muscle mass energy use. The scientists required to have an comprehending of how the protein content material of muscle groups is modified by work out and how it’s regulating the activity of the proteins by way of a chemical reaction known as acetylation. Acetylation can have an effect on protein habits and can take put when acetyl is combining with other molecules.
The scientists enlisted 8 untrained but normally balanced male participants for the study to bear superior-intensity biking teaching for 5 weeks. The members exercised 3 occasions each and every 7 days, completing 4 minutes of cycling at a 90% or a lot more goal rate of their optimum heart amount with a 2-minute relaxation in advance of repeating this sample 4 to 5 occasions for every exercise routine.
Making use of a approach acknowledged as mass spectrometry, they analyzed the composition variations of 3,168 proteins in samples of tissue gathered from the thighs of the individuals in advance of the examine commenced and after the teaching was accomplished. Changes related with 1,263 lysine acetyl-web pages on 464 acetylated proteins ended up also examined.
The analyses uncovered an boost in generation of proteins which are employed for creating the cell’s power making mitochondria, and in proteins associated with the contraction of muscle mass. The scientists also discovered an improve in the acetylation of mitochondrial enzymes and proteins that are associated in cellular electricity generation. Changes in the amount of proteins which reduce the calcium sensitivity of skeletal muscle that is critical for muscle mass contractions have been also noticed.
The research success affirm some well-acknowledged skeletal muscle mass protein alterations that get area pursuing work out, in addition to figuring out new adjustments. For occasion, the calcium sensitivity reduction could demonstrate why the contraction of muscle mass is harder after fatigue sets in. The research also implies that exercising-induced improvements in protein regulation when acetylation usually takes position could lead to boosting metabolic process.
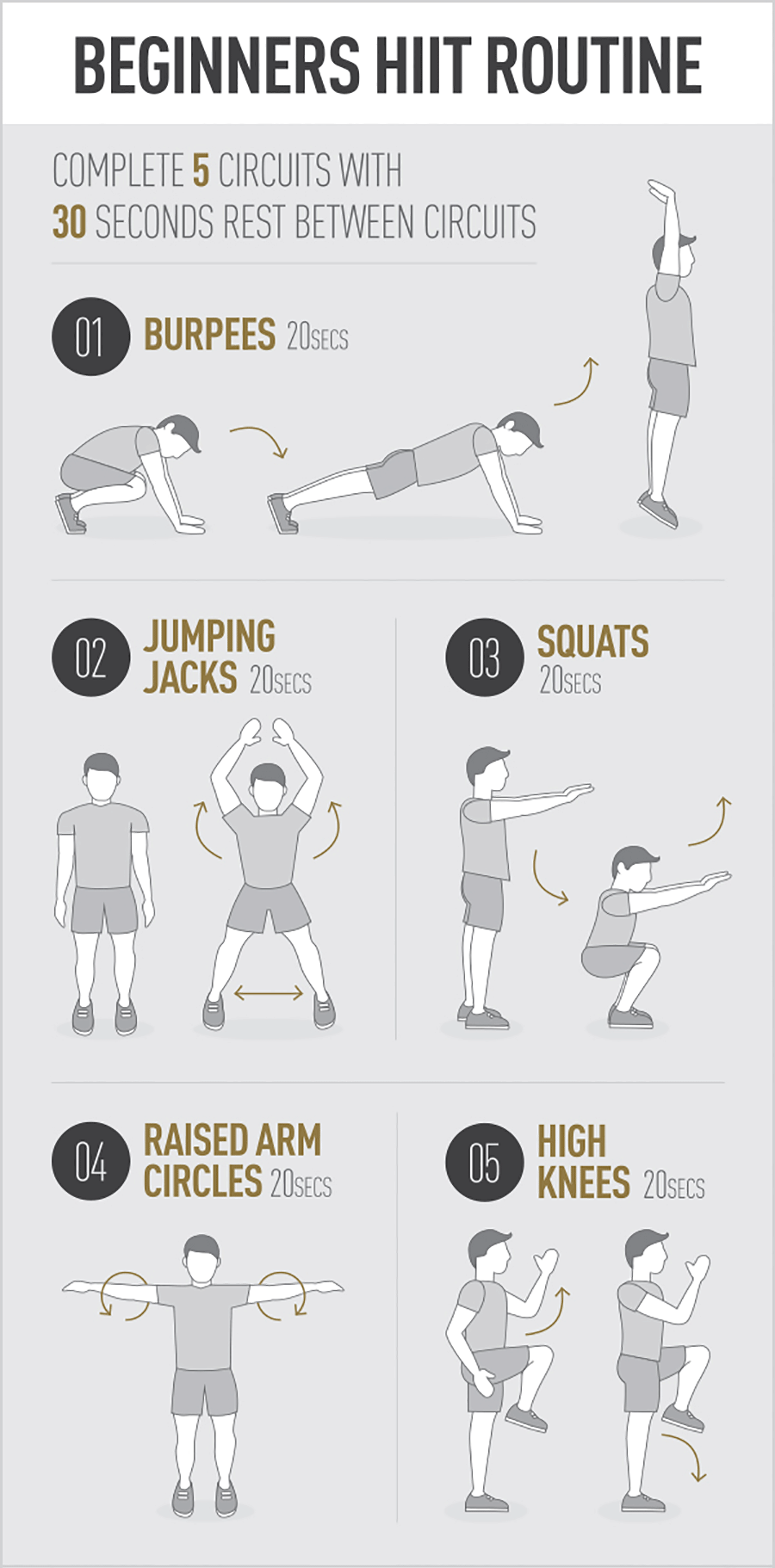
Want to use our images on your website? Ideal click on picture for embed code
[ad_2]
Source website link